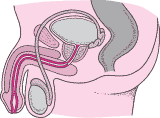
Nursing Care Plan for Deficient Knowledge
Knowledge, deficient regarding condition, treatment program, self-care, and discharge needs related to lack of exposure and information, misinterpretation of information and unfamiliarity with information resources. Deficient Knowledge Definition: Absence or deficiency of cognitive information related to a specific topic Defining Characteristics: Verbalization of the problem; inaccurate follow-through of instruction; inaccurate performance of test; inappropriate or exaggerated behaviors (e.g., hysterical, hostile, agitated, apathetic) Related Factors: Lack of exposure lack of recall information misinterpretation cognitive limitation lack of interest in learning unfamiliarity with information resources Nursing Interventions Nursing Care Plan for Deficient Knowledge 1. Assess ability to learn or perform desired health-related care. Rational : Cognitive impairments need to be identified so an appropriate teaching plan can be designed. 2. Determine client’s learning style especially if cli