Nursing Diagnosis Risk for Infection - NCP Impetigo

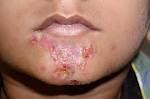
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for infection - NCP Impetigo Nursing Diagnosis Risk for Infection related to decreased immune system, malnutrition, inflammation, and invasive procedures. Expected outcomes are: Clients are free from signs and symptoms of infection. Showed the ability to prevent infection. Demonstrate healthy behavior. Describe the process of transmission of the disease, factors that influence transmission. Nursing Interventions - Nursing Care Plan for Impetigo : Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection. Monitor susceptibility to infection. Limit the visitor when necessary. Instruct patient visitors to wash their hands during a visit and after leaving the patient. Maintain aseptic environment during ongoing treatment. Give skin care in the area epidema. Inspection of skin and mucous membrane of the redness, heat. Inspection of the condition of the wound. Give antibiotic therapy if necessary. Teach how to avoid infection.