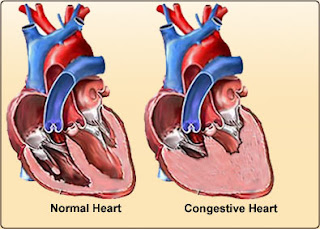
Pathophysiology of Heart Failure

In case of heart failure, the body has several adaptations, both in the heart and systemically. If both ventricular stroke volume is reduced, therefore the emphasis contractility or afterload was increased, the volume and end-diastolic pressure in the two chambers of the heart increased. This will increase the length of myocardial fibers end-diastolic, systolic rise time becomes shorter. If this condition persists, ventricular dilatation occurs. Cardiac output at rest can still be good, but the increase in diastolic pressure that lasts longer / chronicle will spread to both the atrium and the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation. Finally, capillary pressure will increase which will lead to transudation of fluid and edema arising systemic or pulmonary edema. Decrease in cardiac output, especially if associated with a reduction in arterial pressure or decreased renal perfusion, will activate several neural and humoral systems. Increased activity of the sympathetic nervous s...