Nursing Care Plan for Hepatic Cirrhosis / Liver Cirrhosis
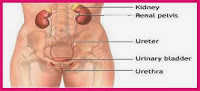
Hepatic cirrhosis is a chronic disease of the liver with inflammation and liver fibrosis which results in the distribution of hepatic structures and loss of most liver function. Major changes that occur due to cirrhosis are the death of liver cells, the formation of fibrotic cells (mast cells), cell regeneration and scar tissue that replaces normal cells (Baradero, 2008).According to Black (2014) liver cirrhosis is a progressive chronic disease characterized by extensive fibrosis (scar tissue) and nodule formation. Cirrhosis occurs when the normal flow of blood, bile and hepatic metabolism is altered by fibrosis and changes in hepatocytes, bile ducts, vascular pathways and reticular cells. Cirrhosis is the final stage in many types of liver injury. Cirrhosis of the liver usually has a nodular consistency, with bundles of fibrosis (scar tissue) and small areas of tissue regeneration. There is extensive damage to hepatocytes. Changes in heart shape change the flow of the vascular and lym...



.jpg)