NCP Hydrocephalus : Acute Pain and Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
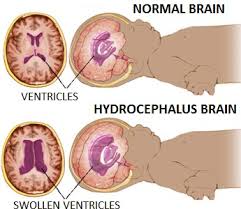
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull, leading to brain swelling. Hydrocephalus is caused by cerebrospinal fluid flow problems, the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. This fluid carries nutrients to the brain, eliminating waste from the brain, and acts as a cushion. CSF normally moves through the area of the brain called ventricles, around the outside of the brain and spinal cord. This fluid is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Fluid buildup can occur in the brain if the flow or absorption is blocked or if too much fluid is produced. Accumulation of fluid puts pressure on the brain, pushing the brain to the skull and damaging or destroying brain tissue. Hydrocephalus - Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions (NIC - NOC) 1. Ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to the increased volume of cerebrospinal fluid. NOC: Circulation status Expected outcomes (NOC): 1. Shows the status of circulation which is characterized by the following indicators: Systolic a...