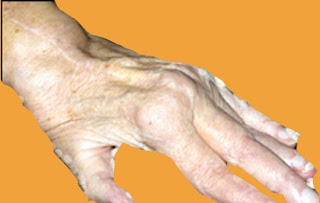
Self Care Deficit Nursing Diagnosis for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Nursing Diagnosis for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Self Care Deficit
related to:
Can be evidenced by:
The expected outcomes / evaluation criteria, patients will:
Nursing Intervention Self Care Deficit Nursing Diagnosis for Rheumatoid Arthritis:
1. Discuss the level of general functioning (0-4) before any onset / exacerbation of the disease and the potential changes that are now anticipated.
Rationale: May be able to resume public activities by performing the necessary adaptation to the current limitations.
2. Maintain mobility, pain control and exercise programs.
Rationale: Support independent physical / emotional.
3. Assess barriers to participation in self-care. Identify / plan for environmental modifications.
Rational: Preparing to improve the independence, which will increase self-esteem.
4. Collaboration: Consult with occupational therapist.
Rationale: Allows you to specify the tools to meet individual needs. Eg, install fasteners, use the tools wear shoes, hanging handle for a shower.
5. Collaboration: Set home health evaluation prior to discharge to the evaluation afterwards.
Rationale: Identify issues that may be encountered due to actual ability level.
6. Collaboration: set consult with other agencies, eg home care services, a nutritionist.
Rationale: It may take a variety of additional assistance for the preparation of the situation at home.
Nursing Diagnosis for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Self Care Deficit
related to:
- Musculoskeletal damage; decreased strength, endurance, pain when moving, depression.
Can be evidenced by:
- Inability to manage daily activities.
The expected outcomes / evaluation criteria, patients will:
- Carry out self-care activities at a level consistent with the ability of the individual.
- Demonstrate technical change / lifestyle to meet the needs of self-care.
- Identify sources of personal / community to meet the needs of self-care.
Nursing Intervention Self Care Deficit Nursing Diagnosis for Rheumatoid Arthritis:
1. Discuss the level of general functioning (0-4) before any onset / exacerbation of the disease and the potential changes that are now anticipated.
Rationale: May be able to resume public activities by performing the necessary adaptation to the current limitations.
2. Maintain mobility, pain control and exercise programs.
Rationale: Support independent physical / emotional.
3. Assess barriers to participation in self-care. Identify / plan for environmental modifications.
Rational: Preparing to improve the independence, which will increase self-esteem.
4. Collaboration: Consult with occupational therapist.
Rationale: Allows you to specify the tools to meet individual needs. Eg, install fasteners, use the tools wear shoes, hanging handle for a shower.
5. Collaboration: Set home health evaluation prior to discharge to the evaluation afterwards.
Rationale: Identify issues that may be encountered due to actual ability level.
6. Collaboration: set consult with other agencies, eg home care services, a nutritionist.
Rationale: It may take a variety of additional assistance for the preparation of the situation at home.

Komentar
Posting Komentar