Nursing Diagnosis Care Plans for Ineffective Airway Clearance
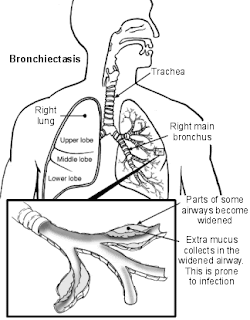
Nursing Diagnosis Care Plans for Bronchiectasis : Ineffective Airway Clearance Ineffective airway clearance related to increased production of secretions, viscous secretions. Purpose: Maintains a patent airway with breath sounds clean. Expected outcomes: Showed behavior to improve airway clearance (effective cough, and issued a secret. Plan of Action: 1. Assess / monitor respiratory frequency. Note the ratio of inspiration and expiration. R /: tachypnea common to some degree can be found at the reception or during stress / acute infection process. Breathing slows down and the frequency of expiratory elongated than inspiration. 2. Auscultation of breath sounds and note the presence of breath sounds. R /: The degree of bronchial spasms occur with airway obstruction and may / not manifested any breath sounds. 3. Assess the patient to a comfortable position, Height head of the bed and sat on the back of the bed. R /: bed head elevation facilitate respiratory function by using gravity. And ...