Nursing Diagnosis Care Plans for Ineffective Airway Clearance
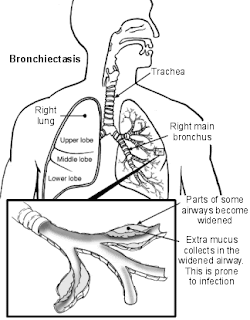
Nursing Diagnosis Care Plans for Bronchiectasis : Ineffective Airway Clearance
Ineffective airway clearance related to increased production of secretions, viscous secretions.
Purpose:
Maintains a patent airway with breath sounds clean.
Expected outcomes:
Showed behavior to improve airway clearance (effective cough, and issued a secret.
Plan of Action:
1. Assess / monitor respiratory frequency. Note the ratio of inspiration and expiration.
R /: tachypnea common to some degree can be found at the reception or during stress / acute infection process. Breathing slows down and the frequency of expiratory elongated than inspiration.
2. Auscultation of breath sounds and note the presence of breath sounds.
R /: The degree of bronchial spasms occur with airway obstruction and may / not manifested any breath sounds.
3. Assess the patient to a comfortable position, Height head of the bed and sat on the back of the bed.
R /: bed head elevation facilitate respiratory function by using gravity. And easier to breathe and helps reduce muscle weakness and can be as a tool chest expansion.
4. Help the patient to practice abdominal breathing or mouth.
R /: To solve and control the dyspnoea and reduce air entrapment.
5. Observation of the characteristic cough and aid measures for effectiveness of cough effort.
R /: Knowing the effectiveness of cough.
6. Depth of fluid intake till 3000ml / day as tolerated and provide a warm heart and fluid intake between meals instead
R /: Hydration helps decrease the viscosity secret, easy warm discharge may decrease bronchial spasms. Liquids between meals can increase gastric distension and pressure diaphragm.
7. Give medication as indicated.
R /: Speeding up the healing process.
Ineffective airway clearance related to increased production of secretions, viscous secretions.
Purpose:
Maintains a patent airway with breath sounds clean.
Expected outcomes:
Showed behavior to improve airway clearance (effective cough, and issued a secret.
Plan of Action:
1. Assess / monitor respiratory frequency. Note the ratio of inspiration and expiration.
R /: tachypnea common to some degree can be found at the reception or during stress / acute infection process. Breathing slows down and the frequency of expiratory elongated than inspiration.
2. Auscultation of breath sounds and note the presence of breath sounds.
R /: The degree of bronchial spasms occur with airway obstruction and may / not manifested any breath sounds.
3. Assess the patient to a comfortable position, Height head of the bed and sat on the back of the bed.
R /: bed head elevation facilitate respiratory function by using gravity. And easier to breathe and helps reduce muscle weakness and can be as a tool chest expansion.
4. Help the patient to practice abdominal breathing or mouth.
R /: To solve and control the dyspnoea and reduce air entrapment.
5. Observation of the characteristic cough and aid measures for effectiveness of cough effort.
R /: Knowing the effectiveness of cough.
6. Depth of fluid intake till 3000ml / day as tolerated and provide a warm heart and fluid intake between meals instead
R /: Hydration helps decrease the viscosity secret, easy warm discharge may decrease bronchial spasms. Liquids between meals can increase gastric distension and pressure diaphragm.
7. Give medication as indicated.
R /: Speeding up the healing process.

Komentar
Posting Komentar